Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) is the process of optimising a website to rank in AI search results. GEO includes optimising content to gain features in AI Overviews, the current AI-generated feature on Google Search, and getting your business referenced and recommended in AI-generated chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google Gemini.
This guide will break down the jargon surrounding GEO, explain where it came from, and what you need to do to rank effectively in AI-driven search. We’ll cover practical steps you can take to optimise your website and search strategy to ensure maximum visibility even when users bypass traditional search engines.
What Is Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimisation, or GEO, is a technique to optimise website content so it’s referenced and prioritised by AI-driven search engines. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on ranking in search engines, GEO helps generative models understand and highlight your content when crafting their outputs.
AI is generating answers, articles, visuals, and more. Generative models don’t rank content in a list like current Google search results; instead, they generate a rich response by incorporating multiple sources. If you want your website to be among the top sources AI presents, GEO is where to invest your marketing budget.
GEO focuses on increasing visibility within these generative responses instead of aiming for a higher rank on a search results page. It prioritises factors like succinctness, relevance, factual accuracy and authority to rank and reference products, services and businesses.
The Origins of the Term ‘Generative Engine Optimisation’
The term “Generative Engine Optimization” (or “optimisation” if you’re on the British side of the pond) evolved naturally from SEO. With the rise of tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, Claude and Perplexity, the need for a new type of optimisation emerged. GEO takes the basics of SEO and adapts them to the requirements of AI-driven search.
The term “Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)” was first used in an academic paper published on arXiv and has started to be used among marketers, content creators, and AI enthusiasts to describe this new style of SEO. It’s a bit jargony, in our opinion, and is not to be confused with “geo” as in “geographical” locations, but it gets the job done.
How Generative Engines Work
Generative models use vast datasets to create responses to user prompts. They don’t rank content in the traditional sense but prioritise the most relevant, credible, and fluent data.
For example, if I ask ChatGPT for a recommendation on the best coffee makers, it will prioritise content that includes direct product comparisons:
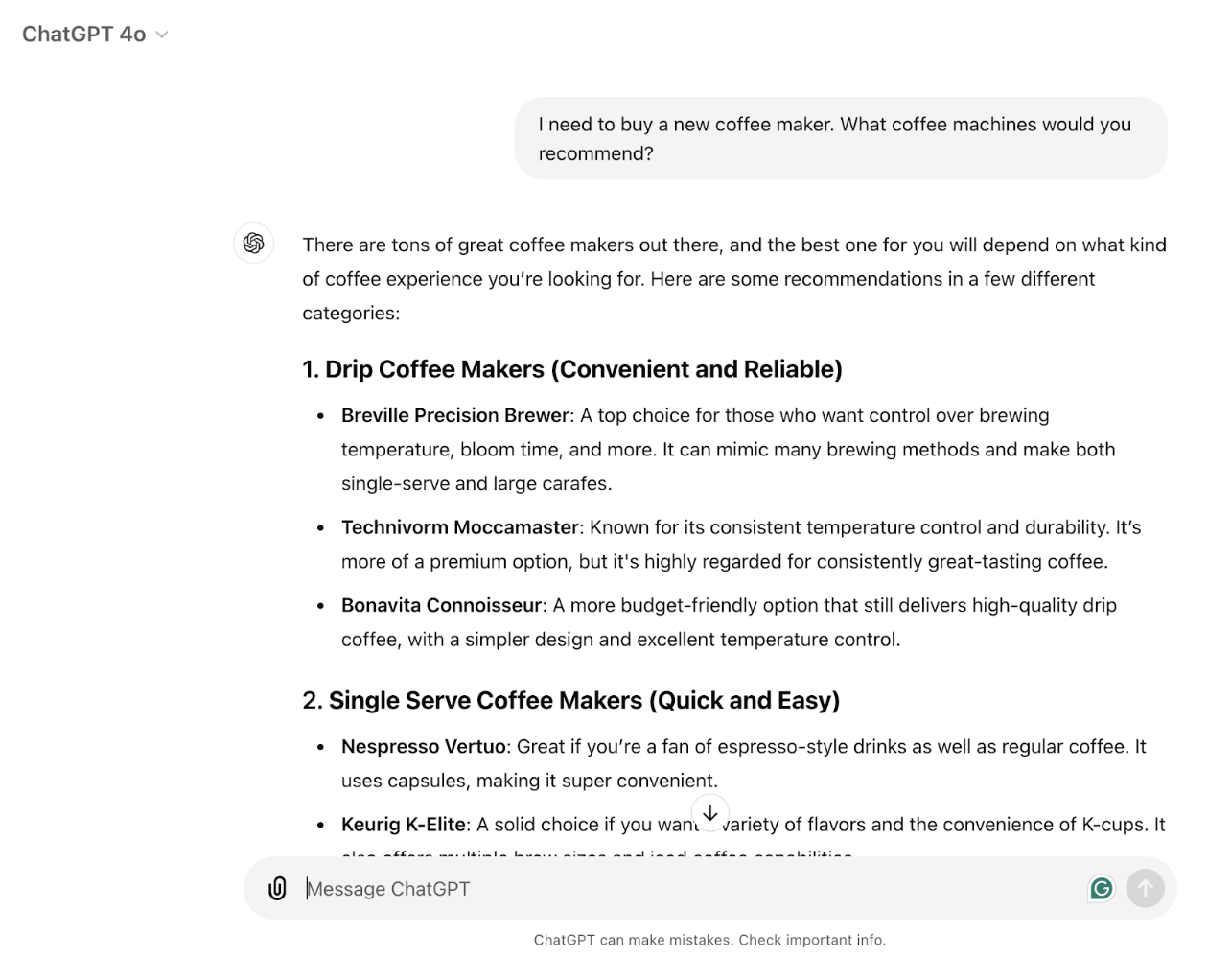
Instead of using keyword density or backlinks, generative models focus on contextual relevance, user intent and the ability to fulfil the user’s query. The way AI evaluates content is different from traditional search engines like Google. It’s all about usefulness and context.
If I give ChatGPT more information about how I like to brew and drink coffee, it uses this context to provide more tailored recommendations:

More detail is needed in website content now to maximise the likelihood of these generative models understanding the specificities, nuances and relevance of your product or service to different types of users.
Struggling to know how to use AI with your marketing?

GEO vs SEO: Similarities and Differences
| Feature | SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) | AI Overviews | GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation) |
| Purpose | Rank content well on search engines like Google. | Provide AI-driven summaries directly in search results. | Optimise content for AI models like ChatGPT to be included in generated responses as well as AI-driven summaries on search results. |
| Key Focus | Keyword optimisation, backlinks, page speed, and other traditional SEO elements. | Formatting content for summarisation, ensuring visibility in search result summaries. | Optimising content to provide context, relevance and authority, ensuring recommendations in generated outputs. |
SEO, AI Overviews (previously SGE) and GEO are the three organic search terms that we are hearing a lot about, but they serve different purposes and use different strategies.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimisation): SEO is the traditional approach to ensuring your content ranks well on search engines like Google. The goal is to rank on search engine results pages (SERPs) when users search for related topics.
- AI Overviews: AI Overviews are the AI-driven summaries directly at the top of search results (previously called SGE or Search Generative Experience). It provides users with quick overviews of information sourced from various web pages.
- GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation): GEO takes optimisation further into the AI realm, focusing on referencing content within generative models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude. GEO is not just about search rankings; it’s about becoming a part of the AI’s knowledge base so your content is favoured during answer generation.
How Is GEO Similar to SEO?
- Visibility Goals: Both GEO and SEO aim to increase the visibility of your content, whether it’s in traditional search engines or AI-generated responses.
- Content Quality: High-quality, authoritative content is crucial for both GEO and SEO. Search engines and generative models favour content that is reliable, informative and well-structured.
- Keyword Strategy: Just like in SEO, GEO involves identifying relevant keywords and phrases to make content easily discoverable by search engines or AI models.
- Technical Optimisation: Both GEO and SEO benefit from a technically optimised website, including proper use of schema markup, metadata and fast page loading times.
- Importance of Backlinks: Backlinks remain important for establishing authority and credibility in both GEO and SEO.
How Is GEO Different from SEO?
- Target Audience: SEO focuses on improving content visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs), whereas GEO aims to have content referenced in AI-generated responses, such as by ChatGPT, Google Gemini and other generative engines.
- Content Presentation: SEO focuses on ranking on search pages where users choose which link to click. GEO aims to have your content directly included in an AI-generated answer, eliminating the need for users to click through multiple links.
- Authority Signals: While SEO relies heavily on keywords, backlinks, and on-page signals, GEO also depends on brand mentions and having information available in trusted aggregators or directories that AI models may prioritise.
- User Intent Handling: SEO focuses on optimising for a wide range of search intents, from informational to transactional. GEO, on the other hand, focuses on optimising for AI-generated answers, which tend to be more informational and less about driving direct traffic.
How to Rank in Generative Engine Optimisation
Want your business recommended more often in generative AI models? We’ve spent a whole lot of time hypothesising, testing and experimenting across industries to understand how to optimise for generative engines. Here are the current theories of how to make it happen:
1. Optimise for Web Search: Many AI tools perform a web search in the background to generate their responses. GEO is built on traditional SEO (yep, spoiler: SEO isn’t dead yet). This means you need to rank in traditional search results to be then picked up by generative models. Essentially, you need to rank well in the old SEO game to be able to play the new GEO game.
Best Practices for Implementing GEO
It’s not just what you do but how you do it. Increasingly, we’re seeing GEO prioritising content that follows these best practices:
- Good Quality: Nobody wants to read crap content. Be detailed, factual and cover topics comprehensively. Include statistics and data points to reinforce credibility. Write a good author bio and include it in the blog post.
- Consistent Brand Voice: A consistent brand voice helps AI recognise your authority and credibility. We’ve found the best way to do this when generating content through AI tools or to even out tone consistency is to feed it a full Brand Accelerator report that includes tone of voice, copy examples and customer personas.
- Simplifies Complex Concepts: Make your content easy to understand. Generative models value fluency and readability, so aim to simplify complex topics while keeping key information intact.
- Skimmable Content: Make your content easy to skim by using headers, bullet points, and visuals. Generative models prefer skimmable content that can be easily summarised.
Is your marketing underperforming?
Integrating GEO with SEO
GEO and SEO work hand-in-hand to increase your content’s visibility across both traditional search engines and AI models. By combining these strategies, you ensure your content ranks well in search engines and is referenced by AI models.
Strategies for Effectively Combining GEO and SEO
To get the best of both worlds, we recommend combining GEO and SEO. Here are the strategies we recommend to effectively integrate GEO and SEO into your marketing strategy:
- Optimise for Both Web Search and AI Context: Focus on ranking well in traditional search engines while ensuring your content is detailed enough for AI models to understand its value and relevance.
- Content for Humans and AI Readability: Create well-structured content that is easy to skim by using clear headings, bullet points and concise paragraphs. This helps with traditional SEO while making your content easier for generative models to summarise and reference.
- Backlinks and Brand Mentions: Go bigger and broader with Digital PR, focusing both on building backlinks and gaining brand mentions across many different websites.
- Monitor Visibility in Both Channels: Track your visibility in and traffic from both traditional SERPs and AI-generated responses.
Does Implementing GEO Actually Work?
Research on the effectiveness of implementing GEO is limited, as it is still a new and emerging field. From our experience at Exposure Ninja, we’ve found that it is effective. We’ve been pioneers in this new type of optimisation, helping clients rank in AI Overviews and teaching other agencies to do the same.
Through using the GEO techniques we discussed above, our Ninja team has secured a whole heap of AI Overview spots for clients across industries. Here’s one example of an AI Overview we’ve secured (and held) for a client in the cleaning sector. This page is consistently the number 1 traffic driver to this client’s website, overtaking the homepage by a lot.
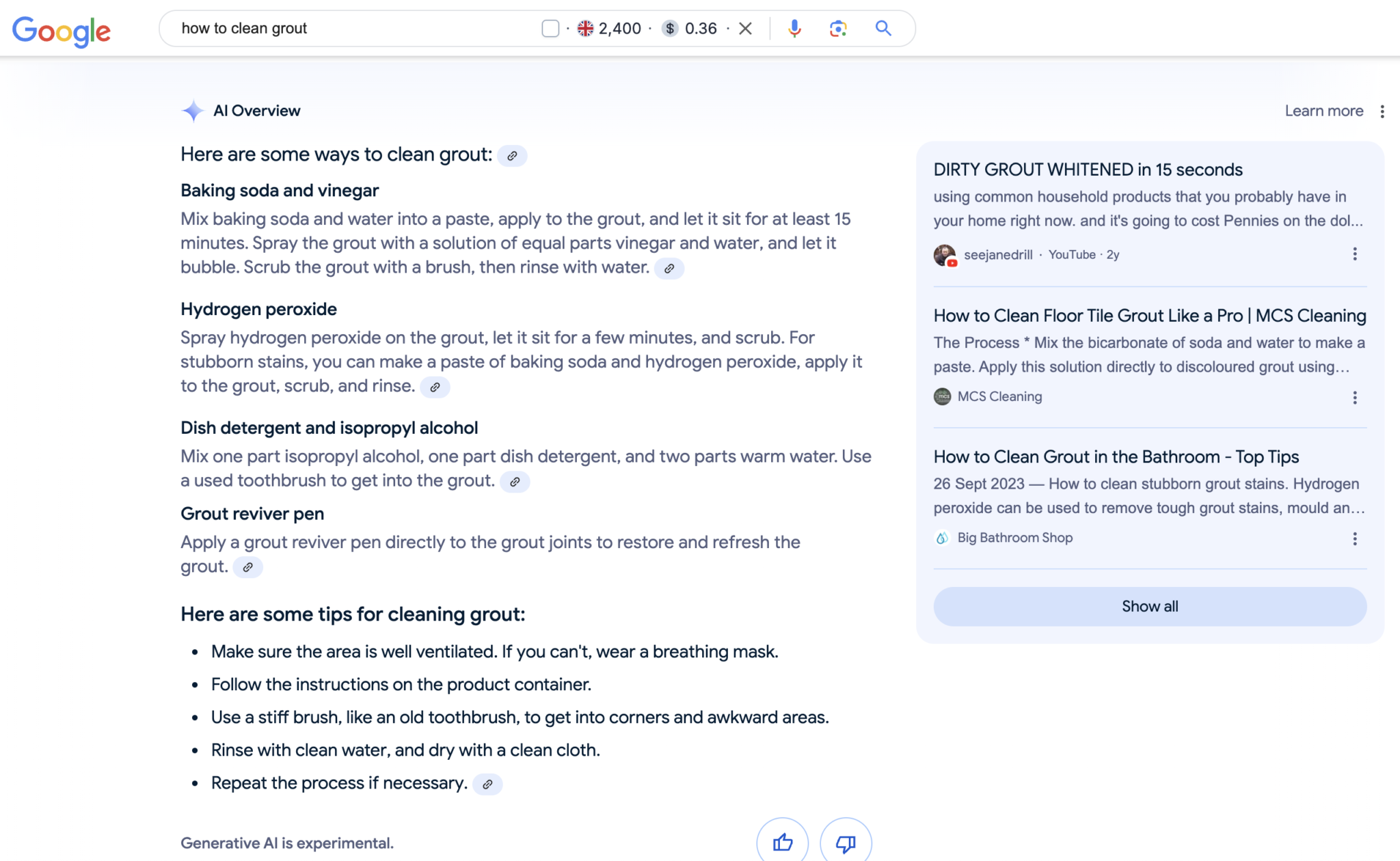
However, we also know that these AI search features and AI chatbots are evolving, and fluctuations happen. Just as with getting the top of Google’s search results, securing AI Overviews or ChatGPT mentions doesn’t mean you’ll maintain them. What marketers can and should do is experiment: figure out how to get them and try different ways to maintain those positions.
We’re not the only ones seeing this. A recent research paper set the SEO world ablaze with its data, finding that implementing GEO techniques can increase visibility in GE responses by up to 40%. The table below from the same paper shows the percentage increases in visibility after making changes to website copy. Greens are new additions, and reds are deletions. Take this relative improvement data with a grain of salt as improvement measures are limited.

Table fromGEO: Generative Engine Optimizationby Aggarwal et al.
How Can You Measure Results from GEO?
Tracking AI Overviews
SEMrush’s Position Tracking tool tracks AI Overview features for keywords tracked for your campaign. Within the Position Tracking tool, navigate to SERP Features and this will display keywords from your campaign that triggered an AI Overview and whether your website was highlighted.
Tracking Visibility
The primary measure currently being used to track generative engine results is overall visibility. This includes general online visibility metrics like backlinks and brand mentions. You can check your backlink profile usingSEMrush’s Backlink Analytics tool. These measures are based on the assumption that the more you’re talked about online, the more likely it is that generative models will include your brand in their responses.
AI Sentiment Analysis
HubSpot has introduced an AI Search Grader tool that measures brand presence by analysing results from GPT-4o. This tool provides a helpful overview of brand sentiment and share of voice.
In practice, the tool runs a series of queries based on the business information you provide, meaning its analysis is limited to the terms you input. However, it can be used repeatedly to evaluate different products or services, giving a more comprehensive insight over time.
Measuring Traffic Referral
The most useful current measure of GEO results are traffic, sessions and conversions on your website that have come through generative engines. At Exposure Ninja, we set up custom reports using your GA4 data to show GEO results. These reports include AI platform traffic over time, AI platform sessions, AI platform conversions, top GEO landing pages and AI platform traffic and conversion splits.
Tracking Mention Frequency
There is no clear way to track mentions and recommendation frequency within AI chatbots. Currently, the only other way to measure mentions is through manual searches on AI engines. This process is time-consuming and — with the rapid evolution of AI search tools — the gathered data can quickly become outdated.
Challenges of GEO
GEO has its own challenges. One major issue is AI’s inherent bias — generative engines are only as good as the datasets they’re trained on. Bias in those datasets can affect which content is generated. So, content should draw on a diverse range of reputable sources and include information representing different perspectives to mitigate bias.
There are also ethical concerns around misinformation and over-optimisation and ensuring factual accuracy in your content is key to avoiding these pitfalls.
AI is evolving rapidly, and staying up-to-date on algorithm changes and new capabilities is crucial to keeping your content visible. Additionally, the winner-takes-all nature of generative models means that only a handful of top responses get the bulk of visibility, making it essential to ensure your content is as authoritative and high-quality as possible.
That’s where Exposure Ninja comes in: we’re pioneers of AI search, having led the way in uncovering ranking factors for and getting our clients featured in AI Overviews and on AI chatbots. We keep on top of all the AI search updates so you can focus on other important stuff in your business. Get your free website and marketing review and find out how we can do the same for you.
The Future of Generative Engine Optimisation
While only a fraction of searches are carried out on AI chatbots and Google still has the vast majority of search market share, some marketers are viewing this moment as a land grab. Integrating GEO into your marketing strategy now puts you ahead of competitors. Many have not yet understood the shift that’s happening.
We Ninjas don’t have a crystal ball here. Still, it’s not absurd to think that generated AI answers could become the primary method for content discovery, especially with its integration into search engines and virtual assistants. If you’re serious about dominating your marketplace, then GEO should be in your game plan.
Move beyond SEO as we know it and get to grips with GEO techniques to future-proof your business
Get GEO insights from our Ninjas by requesting a free website and marketing review. Contact us directly to discuss our Generative Engine Optimisation services.



